Pod II. The Science of Sciences
It is often said by scientists that we build our sciences upon the brainpower of GIANTS. I have done so. First, I have learned my sciences at the feet of GIANTS. Second, I have built my sciences with my own brainpower to meet requirements that the existing sciences could not meet. Always, I have engaged in interdependent processing with GIANTS – in reality where possible, in “virtuality” where not. The simple images that follow represent the evolution of scientific modeling that I discovered (see Figure 1).
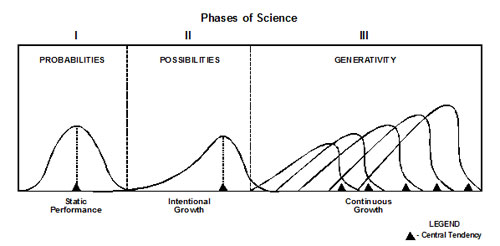
Figure 1. The Evolution of Science Models
In the first phase, we were guided by the image of The Probabilities Science. “The Normal Curve” or “Bell Curve” distributes phenomenal scores equally around some central tendency as a mean, median, or mode (▲). This image allows us to view phenomena in terms of uni-model frequency distributions. Thus, the phenomenal “scores” are plotted on the “X axis” and the frequency of their occurrence on the “Y axis.”
In the second phase, “The Possibilities Science” is modeled with the image of a “Humpbacked Whale.” This image allows us to view phenomena in terms of a “Continuous Curve” moving to incorporate the improved or exemplary performance. Thus, the phenomenal scores are plotted on both the “X” and “Y” axes as the phenomena move toward higher levels of performance.
In the third phase, “Generativity Science” is modeled with multi-modal distributions. This image allows us to view the distribution of phenomena developmentally as they move toward higher levels of performance. Thus, the phenomenal scores are plotted incrementally as they move toward elevated levels of performance.
The Probabilities Science
As I initiated my “Voyage of Discovery,” I found The Probabilities Sciences with which I was indoctrinated to be sufficient for all definable human circumstances. Indeed, The Probabilities Sciences dominated human existence and defined “the conditions” of our scientific experiments. To be sure, for 14 million years, since the first signs of hominid life, humankind, and nature have related to each other through one processing system: S–R Conditioning or reflex responding where there is no intervening processing between the presentation of the stimuli (S), and the emittance of a response (R).
In this context, The Probabilities Science of today was defined by The Parametric Models of Measurement which defined the parametrics of phenomena and projected probabilities for their occurrence. For example, the entire area of parametric statistics evolved from Agrarian Age applications: rows and columns of agriculture were treated differentially. The deviations or variability of phenomenal distributions around some estimate of central tendency were selected to meet environmental or marketplace requirements. Thus, the controlling function of science was enabled by the describing and predicting functions.
| FUNCTIONS | PROCESSING | MEASUREMENT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PROBABILITIES SCIENCE |
|
S–R Conditioned Responding Systems | Parametric Measurement |
The Possibilities Science
As useful as the parametric distribution was for comparison of performance, it is also a powerful source of controlling performance. As we encountered human experiences and endeavors, we found The Probabilities Science limited in its abilities to describe and predict human performance, let alone to control it. Indeed, it was precisely the introduction of The Data Age that led to The Possibilities Science. All of the branching, parallel, and other processing systems of Information Technology or IT are based upon S–O–R Discriminative Learning Systems. They require extraordinary repertoires of conditioned responses with which the human organism (O) discriminates the stimuli (S) and emits the appropriate responses (R).
Possibilities Science is the source of changeability: process-centricity, the continuous processing of all phenomenal dimensions. As such, it creates expanding global possibilities of continuously changing, interdependent, and asymmetrical multidimensional phenomenal vectors. These phenomenal possibilities are due to their processing ability to align with the phenomena in their naturalistic form. In this context, probabilities phenomena occupy a small window of opportunity as “Probabilities Moments” in space and time of the “Possibilities Universes.”
The Possibilities Science addresses the limitations of The Probabilities Model. The critical difference between possibilities and probabilities is found in the quality of the dimensions and their interdependent relationships in continuously evolving processing systems. The operative words are “processing systems:” all dimensions are defined as processing systems. Specifically, the culminating function is to release or free the changeability in phenomena. This requires the highest level of phenomenal information; levels that enable us to relate and empower phenomena in order to release them.
| SCIENCES | FUNCTIONS | PROCESSING | MEASUREMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| POSSIBILITIES |
|
S–O–R Discriminative Processing Systems |
Non-Parametric Measurement |
The Generativity Science
As the universes of possibilities expand, they generate “Possibilities Spaces” or “Phenomenal Spaces,” or opportunities in which the Generativity Science may operate. The Generativity Science is an outgrowth of Possibilities Science. Dedicated exclusively to The Freedom Function, The Generativity Science emphasizes generative processing of all information-modeling components: conceptual, operational, dimensional, vectorial, phenomenal. In other words, The Generativity Science emphasizes expanding the levels of information-modeling before narrowing to the objectives by scaling the values and requirements.
It is with the introduction of The Generativity Science that The Possibilities Science is culminated. To be sure, The Possibilities Scientist, himself released by Generativity, seeks to actualize the Freedom Function for all phenomena. Generativity empowers both scientist and phenomena to process life on their own terms. Generativity is not simply “thinking outside of the box.” Generativity is creating the “cubes” and “spheres” and “social schematics” to fill the “Possibilities Spaces” created by The Possibilities Science. Generativity is creating our own “universes—internal and external” – in which we and the phenomena we are addressing live. In so doing, we employ all manner of GPS™ or Generative Processing Systems,™ individual, organizational, community, cultural, economic. Generativity is “thinking beyond the high-beams.” It is as if we were driving along using our low-beams, then switching to high-beams and seeing things that we would never have otherwise seen. This enables us not only to avoid accidents with the probabilistic obstacles lying ahead of us, but also to get better perspectives on our possibilistic targets or goals. In other words, Generativity Science empowers us to make full use of creating the “Possibilities Spaces” of The Possibilities Universes.
| SCIENCES | FUNCTIONS | PROCESSING | MEASUREMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| GENERATIVITY |
|
S–P–R Generative Processing Systems | Paradigmetric |
The models of science evolve developmentally as does all of nature. In so doing, these models guide us to their own naturalistic development in processing:
- Initiating Probalistically
- Transforming Possibilistically
- Culminating Generatively
You may learn more about the evolution of science in “The Human Sciences.” 1, 2
_________________________
1 Carkhuff, R. R. The Human Sciences. Amherst, MA: HRD Press, 2012.
2 Berenson, B. G. Carkhuff and the Human Sciences. Amherst, MA: HRD Press, 2012.
